Harnessing the Wind: Will You Power Your Portfolio?
Discover the pivotal role of wind energy in the renewable transition. From cost-effective onshore to competitive offshore solutions, explore growth forecasts, innovations, and government commitments driving the industry's trajectory towards doubling by 2030.

We explore the dynamic wind energy market, underscoring its pivotal role in the transition to renewable energy. Our exploration spans the current market landscape, spotlighting the cost-effectiveness of onshore wind and the escalating competitiveness of offshore wind against fossil fuels. Moreover, we delve into the challenges and innovations shaping the sector, including robust growth forecasts and government commitments aimed at expanding wind energy capacity. Noteworthy advancements in offshore wind technology are outlined, alongside growth projections and various solutions. Our conclusion emphasizes the industry's poised trajectory for doubling by 2030, coupled with the potential for sustainable energy progress.
What Makes Wind Power Essential?
The wind power sector has a significant cornerstone place in the overall renewable energy mix in achieving carbon neutrality by 2050, offering both onshore and offshore solutions that cater to diverse energy needs. Onshore wind, having matured significantly over recent years, boasts a well-established global supply chain and a proven track record. This technology has undergone substantial advancements aimed at optimizing electricity generation per megawatt of installed capacity. Innovations such as larger turbines, taller hub heights, and expanded rotor diameters have revolutionized this sector, enabling the exploitation of sites with lower wind speeds.
United States Department of Energy Wind Power
What's The Current State Of The Market?
Overall, the comparison between wind power and fossil fuels demonstrates a clear shift towards renewable energy sources. Onshore wind power has emerged as a cost-effective alternative to fossil fuels, with levelized costs ranging from $30 to $50 per megawatt-hour (MWh), as reported by the United States Department of Energy in 2022. In contrast, offshore wind historically incurred higher upfront costs and maintenance expenses, leading to certain projects becoming infeasible and leading to cancellations or postponements. However, recent auctions and projects have seen offshore wind prices drop below $50 per MWh in certain locations, positioning it as a competitive option (International Energy Agency or IEA, 2022). Compared to coal-fired electricity, which typically costs between $60 and $150 per MWh, and natural gas ranging from $40 to $80 per MWh (IEA, 2022), both onshore and offshore wind offers a compelling advantage over fossil fuels.
The wind energy market is experiencing robust growth, with over 743 gigawatts (GW) of installed capacity globally as of 2023, dominated by onshore wind farms, accounting for approximately 94% of total installed capacity. However, offshore wind capacity has been steadily increasing, reaching 34 GW by the end of 2022, with significant growth projected in the coming years. Despite the promising growth trajectory, challenges persist, notably spiraling costs due to higher deployment costs due to inflation and higher interest rates for financing developments which has led to project cancellations, for example, in the United States and Britain.
To address these challenges, there has been a notable adjustment in the pricing of power purchase agreements (PPAs) and government-backed contracts known as Contracts for Difference. This price reset aims to ensure the economic viability of offshore wind projects and facilitate their sustainability amidst economic uncertainties. Although offshore wind costs, for example in Europe, are gradually declining and becoming more competitive, with prices falling close to $50/MWh in nearshore bottom-fixed wind auctions in the North Sea, the United States market still faces economic challenges, with offshore wind costing over $85/MWh. Nonetheless, technological innovations offer the potential for substantial cost reduction, indicating a promising outlook for the offshore wind sector.
Which Countries Are Leading?
Several countries are leading the wind sector, boasting significant installed capacity and substantial investments in wind energy infrastructure. Countries pursue wind energy projects for several reasons, including the transition to renewable energy sources, enhancing energy security, stimulating economic growth and job creation, achieving environmental benefits, driving technological innovation, meeting climate targets, and promoting regional development.
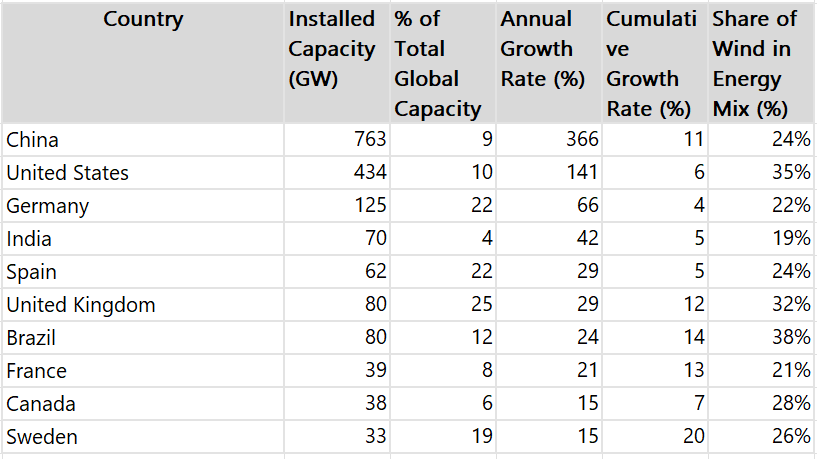
The following table summarizes the installed wind energy capacity for various leading countries, along with their respective percentages of the total global capacity, annual growth rates, cumulative growth rates, and the share of wind energy in their overall energy mix.
Challenges Will Drive Innovation
Despite its promising growth trajectory, the wind energy market faces several challenges, including grid integration issues, permitting and regulatory hurdles, supply chain constraints, and public opposition in some areas. However, these challenges also present opportunities for innovation and collaboration within the industry and among stakeholders. By addressing these obstacles, the wind energy sector can unlock its full potential and play a more significant role in the global energy transition.

Advancements in technology and approaches play a crucial role in improving offshore wind projects and enhancing their efficiency, reliability, and overall performance. Below is a summary of some of the key industry initiatives:
- Larger and more efficient turbines: Technological advancements have enabled the development of larger wind turbines with increased power generation capacity. These turbines can capture more energy from the wind, leading to higher electricity output per turbine and reducing the overall number of turbines needed for a project.
- Grid connection and transmission improvements: Improving grid connection and transmission infrastructure ensures the efficient transfer of electricity generated by offshore wind farms to onshore grids. Upgrades in grid connection technology reduce energy losses during transmission and enhance the overall reliability of the electricity supply.
- Floating offshore wind technology: Floating offshore wind technology allows wind turbines to be installed in deeper waters where fixed-bottom foundations are not feasible. This technology expands the geographical scope for offshore wind development and unlocks new areas with abundant wind resources, thereby increasing the overall potential for offshore wind energy generation.
- Energy storage solutions: Energy storage solutions, such as batteries, pump storage, or hydrogen production, enable the storage of surplus electricity generated by offshore wind farms during periods of low demand. This stored energy can be utilized during peak demand periods or when wind conditions are unfavorable, improving the stability and flexibility of the electricity grid.
- Digitalization and automation: Digitalization and automation technologies optimize the operation and maintenance of offshore wind turbines, reducing downtime, enhancing performance monitoring, and enabling predictive maintenance. These technologies utilize data analytics, remote monitoring, and artificial intelligence to improve overall efficiency and reliability.
- Power-to-X technologies: Power-to-X technologies involve the conversion of excess electricity generated by offshore wind farms into other forms of energy, such as hydrogen, synthetic fuels, or heat. These technologies provide opportunities for energy storage, grid balancing, and the production of renewable fuels for transportation and industrial applications, contributing to the decarbonization of various sectors.
- Environmental monitoring and mitigation: Advanced environmental monitoring systems help offshore wind developers assess and mitigate the potential environmental impacts of their projects. These systems monitor marine ecosystems, wildlife habitats, and underwater noise levels to ensure compliance with environmental regulations and minimize adverse effects on marine life.
- Supply chain development: Strengthening the offshore wind supply chain through investments in manufacturing, logistics, and workforce development improves project efficiency and reduces costs. A robust supply chain ensures timely delivery of components, reduces dependency on imports, and supports local economies, fostering sustainable growth in the offshore wind industry.
- Policy and regulatory frameworks: Clear and supportive policy and regulatory frameworks provide a stable and predictable environment for offshore wind investment and development. Well-defined regulations, incentives, and permitting processes streamline project development, attract investment, and mitigate risks for stakeholders.
- International collaboration and knowledge sharing: Collaboration among governments, industry stakeholders, and research institutions facilitates knowledge sharing, technology transfer, and best practice dissemination across borders. International cooperation enables the exchange of expertise, fosters innovation, and accelerates the deployment of offshore wind projects worldwide, contributing to global energy transition efforts.
Growth Projections
The future looks bright for the wind energy market, with robust growth projected in the coming years. According to the IEA, global wind capacity is expected to nearly double by 2030, reaching over 1,400 GW. This growth will be driven by increasing demand for clean energy, declining costs of wind power generation, and supportive government pricing and financial incentives and policies aimed at reducing greenhouse gas emissions and combating climate change.

Government Commitments
Government commitments to wind power generation represent significant strides toward the global energy transition, aligning with broader renewable energy strategies worldwide. These commitments, spanning funding, financial incentives, and supportive policies for both onshore and offshore wind, reflect a collective effort to mitigate climate change and reduce dependence on fossil fuels. Below is a summary of some of the regional initiatives.
The European Union (EU), for instance, aims to boost onshore and offshore wind capacity to 300 GW by 2050, supported by funding from the European Regional Development Fund and the European Investment Bank. Policies such as the Renewable Energy Directive and the Clean Energy for All Europeans Package further bolster wind power initiatives in the EU.
In the United States, President Biden has set a target of deploying 30 GW of offshore wind by 2030, alongside backing for onshore wind expansion. Financial incentives like federal tax credits with the Inflation Reduction Act and investment grants are available to support wind energy projects, with additional incentives provided by states like California and New York. The United States also implements renewable portfolio standards in several states to mandate a minimum share of electricity from renewable sources, including wind.
China has committed to increasing both onshore and offshore wind power capacity, aiming for renewable energy to comprise 50% of its total energy consumption by 2050. The Chinese government offers substantial subsidies, feed-in tariffs, and low-interest loans to support wind projects, underpinned by policies like the Renewable Energy Law and the National Wind Power Planning.
India has set ambitious targets for onshore and offshore wind power capacity expansion, supported by funding through subsidies, generation-based incentives, and tax benefits. Policies like the National Wind-Solar Hybrid Policy and the National Offshore Wind Energy Policy promote wind energy development in India.
These initiatives have delivered and continue to offer the potential to create jobs across all political parties, fostering economic growth and development. By promoting renewable energy projects, governments can generate employment opportunities in various sectors, from manufacturing and construction to research and development. This inclusive approach to job creation underscores the bipartisan nature of renewable energy initiatives and their positive impact on local economies.
Overall, as countries continue to prioritize wind power generation as part of their renewable energy agendas, they not only contribute to the global energy transition but also stimulate job growth and foster economic resilience across diverse political landscapes.

Consider Wind Energy In Your Investment
In conclusion, the wind energy market is poised for continued growth and innovation, driven by a combination of technological advancements, decreasing costs, and supportive government policies. With over 743 GW of installed capacity globally, which represents approximately 12% of the total energy mix and ambitious targets set for the future, wind energy is playing an increasingly significant role in meeting the world's growing energy needs while mitigating climate change. As the industry continues to evolve, we can expect to see even greater contributions from wind power towards a sustainable and environmentally friendly energy future.
Fun Fact
Did you know that the world's largest offshore wind farm, the Hornsea One project, located off the coast of Yorkshire, England, covers an area larger than the city of Paris? With its 174 wind turbines, it can generate enough electricity to power over one million homes. That's enough clean energy to light up an entire city with the power of the wind!
Free Newsletter Content
Twice a month with our newsletter distribution, we will discuss the market trends in one of our six themes below:
1. Renewable Energy (think solar, wind, hydroelectric)
2. Resources (think hydrogen)
3. Circular Economy (think water)
4. Energy Storage (think battery power grid)
5. Carbon Capture and Storage (think Carbon dioxide CO2 capture)
6. Green Transportation (think electric vehicles)
Premium Newsletter Summary
With paid Premium content, you can access our select investments now. They are ready to invest today with no minimum investment amounts and they are accessible in established liquid stock markets to easily buy or sell your investments at any time. Make it your monthly habit!
We also include their Environmental, social, and governance (ESG) scores. The ESG data focuses on sustainability, diversity, human rights, license to operate, business ethics, and corporate governance. Using 630 metrics, ESG scores provide a comparison of a company's practices with their industry peers. The higher the score the better the company in their peer group.
Return Habit donates 2% of annual profits to underserved communities for green jobs and education. These jobs and training are critical for our community and economy.
Refer to www.returnhabit.com for our terms and conditions.

